9. Labour market discrimination
KAT.TAL.322 Advanced Course in Labour Economics
September 22, 2025
Same level of productivity, different outcomes based on nonproductive characteristics
Employers may discriminate in hiring/firing decisions
Co-workers may discriminate in collaboration activity
Customers may discriminate in purchase decisions
Taste discrimination
Taste discrimination
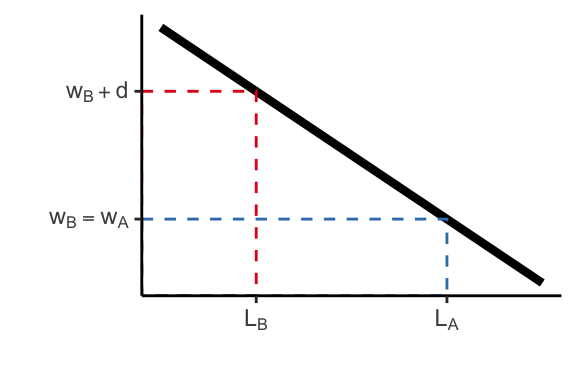
First formalized by Becker (1957)
- There are two types of workers \(A\) and \(B\)
- Perfect substitutes: \(F(A + B) \Rightarrow F_A = F_B\)
A firm decides how many workers to employ to maximise the utility
\[ \max_{A, B} PF(A + B) - w_A A - w_B B - d B \]
where \(d \geq 0\) is the disutility employer gets from worker \(B\)
Taste discrimination
FOCs:
\[\begin{align} PF_A(A + B) &= w_A \\ PF_B(A + B) &= w_B + d \end{align}\]
Hire \(B\) iff \(w_B + d \leq w_A\)
Taste discrimination
Perfect competition and free entry
Non-discriminating firms \(d = 0\) enters the market
Pay competitive wages to both groups \(w_A = w_B = P F_L(L)\)
Therefore,
- discriminating firms hire \(A\) workers at \(w_A\)
- non-discriminating firms hire everyone at \(w_A = w_B = w\)
Taste discrimination cannot persist under perfect competition
Taste discrimination
Imperfect competition
Monopsonistic employer
Lower wages and lower employment of discriminated group
Market frictions (Black 1995)
Job search costs:
- Existence of employers with \(d>0\) lowers reservation wage
- Wages of discriminated workers at non-discriminating firms are also lower
- Longer unemployment until meet non-discriminating firm
Statistical discrimination
Statistical discrimination
Overview
Key feature: unobservable productivity
- Suppose firms meets workers \(A_i\) and \(B_j\) such that \(F_{Ai} = F_{Bi}\)
- Firm doesn’t see \(F_{Ai}\) or \(F_{Bi}\), only group identities \(A\) and \(B\)
- If firms believe that \(\mathbb{E}(F_A) \geq \mathbb{E}(F_B)\), then \(\uparrow w_A\) and \(\uparrow L_A\)
Statistical discrimination
Two types of workers: high \(h^+ > 0\) and low \(h^- = 0\)
Employers know the overall share of efficient workers \(\pi(h^+) \equiv \pi\)
Employers use costless test to infer worker types and hire if passed
- \(\Pr(\text{pass} | h^+) = 1\)
- \(\Pr(\text{pass} | h^-) = p\) where \(p \in [0, 1]\)
Average productivity of workers passing the test (\(\equiv w\))
\[ w \equiv \mathbb{E}\left(h | \text{pass}\right) = h^{+}\frac{\pi}{\pi + p\left(1 - \pi\right)} \]
Statistical discrimination
Self-fulfilling prophecies
Workers choose education to \(\max_{e\in\{0, 1\}} U(w, e) = \max_e w - e\)
If \(e = 1 \Rightarrow\) achieve productivity \(h^+\), otherwise, \(h^-\)
\[ \begin{align} w^{+} \equiv \mathbb{E}\left(h | \text{pass}\right) &= h^+ \frac{\pi}{\pi + p(1 - \pi)} \\ \mathbb{E}\left(w | e = 0\right) &= p w^{+} \end{align} \]
Optimal decision \(e = 1 \Leftrightarrow w^{+} - 1 \geq \mathbb{E}\left(w | e = 0 \right) \Rightarrow p \leq \pi\left[\left(h^{+} - 1\right)\left(1 - p\right)\right]\)
Statistical discrimination
Multliple equilibria and persistent inequalities

Source: Figure 5.7 (Cahuc 2004)
Systemic discrimination
Systemic discrimination (Bohren, Hull, and Imas 2025)
Discrimination in one area has spillover effects on other areas
Let’s consider two programmers: male (M) and female (F)
flowchart LR C["<span style='font-size:20px !important'>Programmers</span><br><i class='bi bi-person-standing' style='color:#107895'> <i class='bi bi-person-standing-dress' style='color: #8e2f1f'></i>"] classDef default color: #000000, fill:transparent, stroke: transparent, padding: 0px !important, font-size: 34px linkStyle default stroke: #000000, stroke-width:2px;
Systemic discrimination (Bohren, Hull, and Imas 2025)
Discrimination in one area has spillover effects on other areas
They submit codes \(C_{0M} \equiv C_{0F}\) to open-source software
flowchart LR C["<span style='font-size:20px !important'>Programmers</span><br><i class='bi bi-person-standing' style='color:#107895'> <i class='bi bi-person-standing-dress' style='color: #8e2f1f'></i>"] G["<span style='font-size:20px !important'>Open-source contributions</span><br><i class='bi bi-github' style='font-size: 28px'></i><br><i class='bi bi-person-standing' style='color: #107895'> <i class='bi bi-person-standing-dress' style='color: #8e2f1f'></i><br><i class='bi bi-file-earmark-code' style='color:grey'></i> <i class='bi bi-file-earmark-code' style='color:grey'></i>"] C --> G classDef default color: #000000, fill:transparent, stroke: transparent, padding: 0px !important, font-size: 34px linkStyle default stroke: #000000, stroke-width:2px;
Systemic discrimination (Bohren, Hull, and Imas 2025)
Discrimination in one area has spillover effects on other areas
They receive performance ratings \(\color{#107895}{P_M}\) and \(\color{#8e2f1f}{P_F}\)
flowchart LR C["<span style='font-size:20px !important'>Programmers</span><br><i class='bi bi-person-standing' style='color:#107895'> <i class='bi bi-person-standing-dress' style='color: #8e2f1f'></i>"] G["<span style='font-size:20px !important'>Open-source contributions</span><br><i class='bi bi-github' style='font-size: 28px'></i><br><i class='bi bi-person-standing' style='color: #107895'> <i class='bi bi-person-standing-dress' style='color: #8e2f1f'></i><br><i class='bi bi-file-earmark-code' style='color:grey'></i> <i class='bi bi-file-earmark-code' style='color:grey'></i>"] E["<span style='font-size:20px !important'>Evaluations</span><br><i class='bi bi-thermometer-high' style='color: #107895'></i> <i class='bi bi-thermometer-low' style='color: #8e2f1f'></i>"] C --> G --> E classDef default color: #000000, fill:transparent, stroke: transparent, padding: 0px !important, font-size: 34px linkStyle default stroke: #000000, stroke-width:2px;
Systemic discrimination (Bohren, Hull, and Imas 2025)
Discrimination in one area has spillover effects on other areas
Apply for jobs with signals \(\color{#107895}{S_M} = (\color{#107895}{P_M}, R_M)\) and \(\color{#8e2f1f}{S_F} = (\color{#8e2f1f}{P_F}, R_F)\)
flowchart LR C["<span style='font-size:20px !important'>Programmers</span><br><i class='bi bi-person-standing' style='color:#107895'> <i class='bi bi-person-standing-dress' style='color: #8e2f1f'></i>"] G["<span style='font-size:20px !important'>Open-source contributions</span><br><i class='bi bi-github' style='font-size: 28px'></i><br><i class='bi bi-person-standing' style='color: #107895'> <i class='bi bi-person-standing-dress' style='color: #8e2f1f'></i><br><i class='bi bi-file-earmark-code' style='color:grey'></i> <i class='bi bi-file-earmark-code' style='color:grey'></i>"] E["<span style='font-size:20px !important'>Evaluations</span><br><i class='bi bi-thermometer-high' style='color: #107895'></i> <i class='bi bi-thermometer-low' style='color: #8e2f1f'></i>"] J["<span style='font-size:20px !important'>Job application</span><br><i class='bi bi-buildings' style='font-size: 28px'></i><br><i class='bi bi-person-standing' style='color: #107895'> <i class='bi bi-person-standing-dress' style='color: #8e2f1f'></i><br><i class='bi bi-file-earmark-person' style='color:grey'></i> <i class='bi bi-file-earmark-person' style='color:grey'></i><br><i class='bi bi-thermometer-high' style='color: #107895'></i> <i class='bi bi-thermometer-low' style='color: #8e2f1f'></i>"] C --> G --> E --> J C --> J classDef default color: #000000, fill:transparent, stroke: transparent, padding: 0px !important, font-size: 34px linkStyle default stroke: #000000, stroke-width:2px;
Systemic discrimination (Bohren, Hull, and Imas 2025)
Discrimination in one area has spillover effects on other areas
Employer’s hiring decision \(\color{#107895}{A_M(M, S_M)}\) and \(\color{#8e2f1f}{A_F(F, S_F)}\)
flowchart LR C["<span style='font-size:20px !important'>Programmers</span><br><i class='bi bi-person-standing' style='color:#107895'> <i class='bi bi-person-standing-dress' style='color: #8e2f1f'></i>"] G["<span style='font-size:20px !important'>Open-source contributions</span><br><i class='bi bi-github' style='font-size: 28px'></i><br><i class='bi bi-person-standing' style='color: #107895'> <i class='bi bi-person-standing-dress' style='color: #8e2f1f'></i><br><i class='bi bi-file-earmark-code' style='color:grey'></i> <i class='bi bi-file-earmark-code' style='color:grey'></i>"] E["<span style='font-size:20px !important'>Evaluations</span><br><i class='bi bi-thermometer-high' style='color: #107895'></i> <i class='bi bi-thermometer-low' style='color: #8e2f1f'></i>"] J["<span style='font-size:20px !important'>Job application</span><br><i class='bi bi-buildings' style='font-size: 28px'></i><br><i class='bi bi-person-standing' style='color: #107895'> <i class='bi bi-person-standing-dress' style='color: #8e2f1f'></i><br><i class='bi bi-file-earmark-person' style='color:grey'></i> <i class='bi bi-file-earmark-person' style='color:grey'></i><br><i class='bi bi-thermometer-high' style='color: #107895'></i> <i class='bi bi-thermometer-low' style='color: #8e2f1f'></i>"] H["<span style='font-size:20px !important'>Hired?</span><br><i class='bi bi-check-circle' style='color:#107895'></i> <i class='bi bi-x-circle' style='color:#8e2f1f'></i>"] C --> G --> E --> J --> H C --> J classDef default color: #000000, fill:transparent, stroke: transparent, padding: 0px !important, font-size: 34px linkStyle default stroke: #000000, stroke-width:2px;
Decomposition (Bohren, Hull, and Imas 2025)
Direct discrimination
For a given signal \(S\), \(\delta(S) \equiv A(M, S) - A(F, S) \neq 0\)
Total discrimination
Let \(G(A | C_0, i)\) be distribution over all possible actions given identity \(i\) and initial condition \(C_0\).
\[ \Delta^T(C_0) \equiv \mathbb{E}_G\left[A | C_0, M\right] - \mathbb{E}_G\left[A | C_0, F\right] \neq 0 \]
Systemic discrimination
Let \(\tilde{G}(A|C_0, i)\) be distribution over actions under original signal distribution but \(A(-i, S)\)
\[ \Delta^S(C_0, M) \equiv \mathbb{E}_G\left[A | C_0, M\right] - \mathbb{E}_\tilde{G}\left[A, C_0, F\right] \]
\[ \Delta^S(C_0, F) \equiv \mathbb{E}_\tilde{G}\left[A | C_0, M\right] - \mathbb{E}_G\left[A, C_0, F\right] \]
Decomposition
Let \(\Sigma(S | C_0, i)\) be distribution over all possible signals given identity \(i\) and initial condition \(C_0\)
\[ \Delta^T(C_0) = \mathbb{E}_\Sigma\left[\delta(S)|C_0, M\right] + \Delta^S(C_0, F) \]
\[ \Delta^T(C_0) = \mathbb{E}_\Sigma\left[\delta(S) | C_0, F\right] + \Delta^S(C_0, M) \]
Empirical results
Measuring discrimination
\(\Delta\) Wage by non-productive characteristics given same productivity.
Empirical challenges
- What constitutes a productive vs non-productive characteristic?
- Is \(\Delta\) wage attributable to discrimination alone or worker preferences?
- Does the discrimination arise from tastes or unobserved information?
Types of studies
- Observational
- Audit and correspondence studies
- Lab and field experiments
- Quasi-random variation
Kitagawa-Oaxaca-Blinder1 decomposition
Wages in two groups (\(A\) and \(B\)) can be written
\[ \begin{align} \ln w_A &= \mathbf{x}_A \boldsymbol{\beta}_A + \varepsilon_A, \quad \mathbb{E}\left(\varepsilon_A\right) = 0 \\ \ln w_B &= \mathbf{x}_B \boldsymbol{\beta}_B + \varepsilon_B, \quad \mathbb{E}\left(\varepsilon_B\right) = 0 \\ \end{align} \]
Then, average wage differential
\[ \Delta \equiv \mathbb{E}\left(\ln w_A\right) - \mathbb{E}\left(\ln w_B\right) = \color{#288393}{\left[\mathbb{E}\left(\mathbf{x}_A\right) - \mathbb{E}\left(\mathbf{x}_B\right)\right]\boldsymbol{\beta}_A} + \color{#9a2515}{\mathbb{E}\left(\mathbf{x}_B\right)\left(\boldsymbol{\beta}_A - \boldsymbol{\beta}_B\right)} \]
decomposed into explained and unexplained components.
Kitagawa-Oaxaca-Blinder decomposition
Interpretation
- Common support: \(\mathbf{x}_A\) and \(\mathbf{x}_B\) contain same set of variables with similar value
- Conditional mean independence: \(\mathbb{E}(\varepsilon_A | \mathbf{x}_A) = \mathbb{E}(\varepsilon_B | \mathbf{x}_B) = 0\)
- Invariance of conditional distributions: distribution of \(w_A | \mathbf{x}_A\) remains unchanged if \(B\) workers receive returns \(\boldsymbol{\beta}_A\)
These are very strict assumptions, so the decomposition is a correlational (not causal) measure.
Kitagawa-Oaxaca-Blinder decomposition
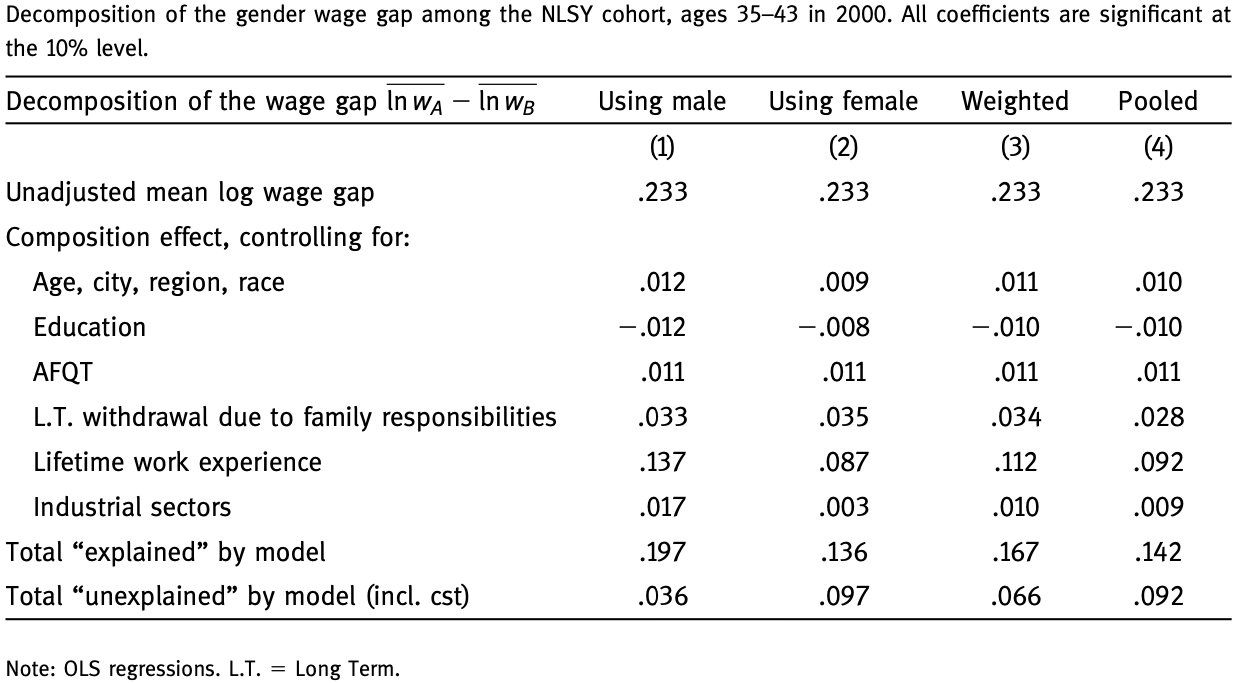
Source: Table 8.5 (Cahuc 2004)
Audit (correspondence) studies
- Send fictitious CVs nearly identical except in group membership
- Measure callback (interview invitations, offers) received
- RCT \(\Rightarrow\) group differences can be interpreted as discrimination
Challenges
- CVs may not convey all relevant productive characteristics
- Cannot disentangle taste discrimination from statistical
- Harder to generalize
Bertrand and Mullainathan (2004)
Created templates for CVs of jobseekers in Boston and Chicago
- high and low quality types based on experience, skills, career profiles
- randomly assign distinctively White or African-American name
- track callback/email rates in race/sex/city/quality cell
| White names | African-American | |
|---|---|---|
| College degree | 0.720 | 0.720 |
| (0.450) | (0.450) | |
| Years of experience | 7.860 | 7.830 |
| (5.070) | (5.010) | |
| Computer skills? | 0.810 | 0.830 |
| (0.390) | (0.370) | |
| Obs. | 2 435 | 2 435 |
Source: Table 3 (Bertrand and Mullainathan 2004)
Bertrand and Mullainathan (2004)
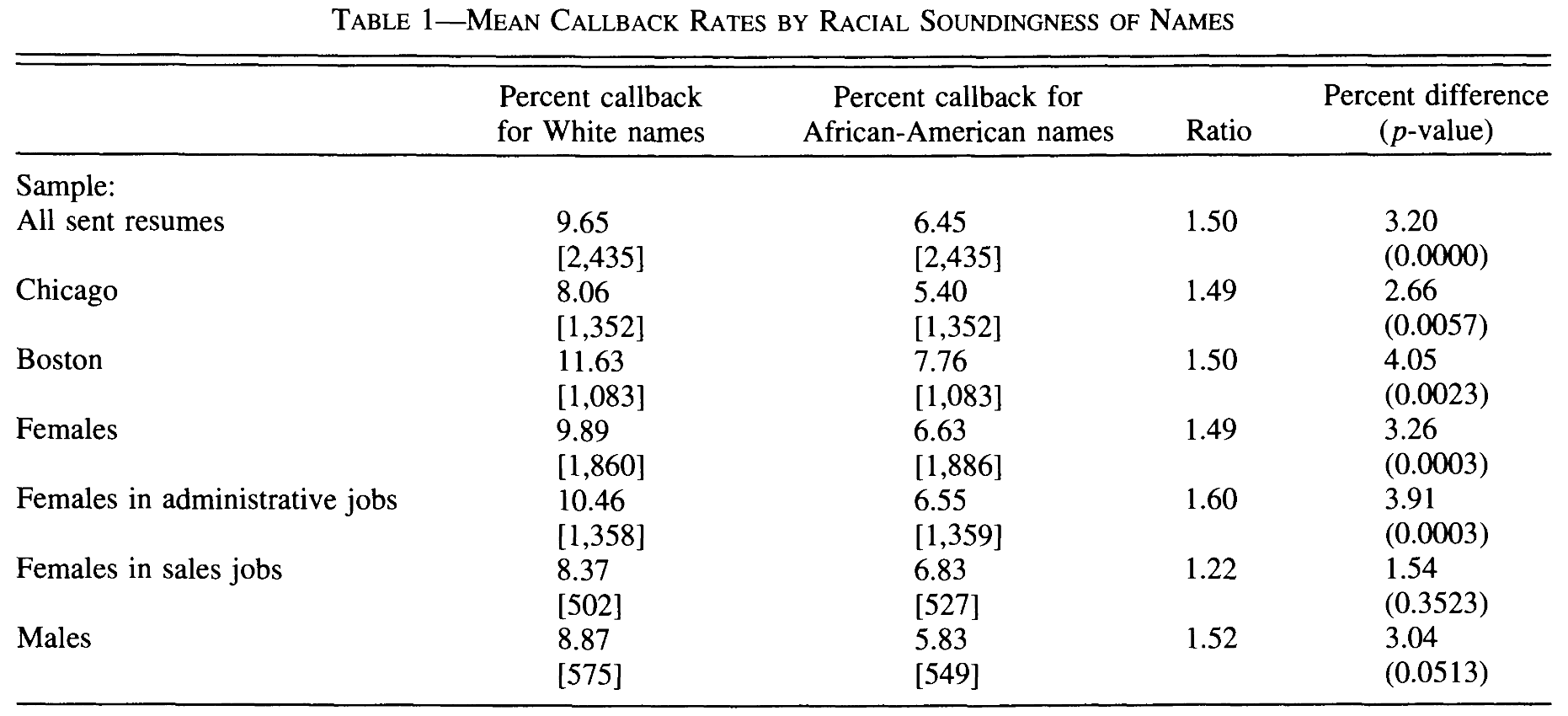
Goldin and Rouse (2000)
Pre-1970s, musicians handpicked by the director
In 1970s-80s, auditions
- “open and routinized”
- blind (some stages)
Staggered adoption of screen: DiD method
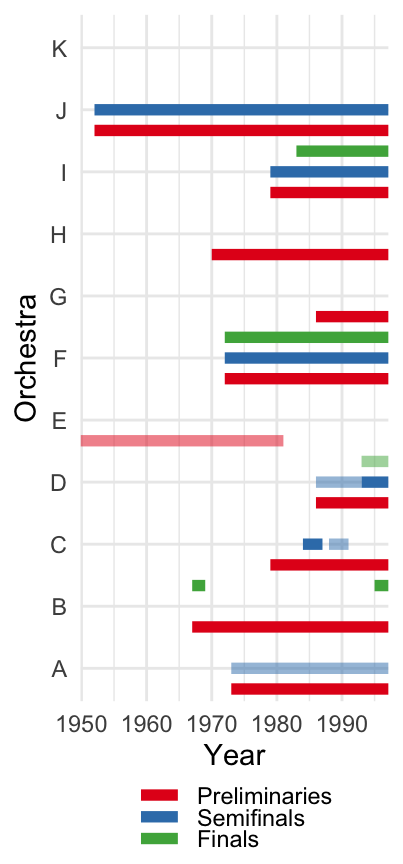
Goldin and Rouse (2000)
Results
| Preliminaries | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without semifinals | With semifinals | Semifinals | Finals | |
| Female x Blind | 0.111 | -0.025 | -0.235 | 0.331 |
| (0.067) | (0.251) | (0.133) | (0.181) | |
| Obs. | 5 395 | 6 239 | 1 360 | 1 127 |
| R2 | 0.775 | 0.697 | 0.794 | 0.878 |
Source: Table 6 (Goldin and Rouse 2000)
Mobius and Rosenblat (2006)
Lab experiment: taste discrimination based on beauty
Participants randomly assigned as workers (5) and employers (5).
Workers answer survey and solve simplest maze game
Survey + practice time = digital CV
Confidence: predict # mazes solved in 15 min (private)
\(100 A_j - 40 |C_j - A_j|\), where \(A_j\) actual and \(C_j\) predicted performance
Mobius and Rosenblat (2006)
Workers randomly matched to employers (\(5\times5\))
B CV only (baseline) V CV + (visual) O CV + (oral) VO CV + + (visual and oral) FTF CV + + (face-to-face) Employers set wages \(w_{ij}\) = # mazes could solve in 15 min \(\Pi_i = 4000 - 40 \sum_{j=1}^5 |w_{ij} - A_j|\)
Workers complete 15 min “employment”: realised \(A_j\)
Mobius and Rosenblat (2006)
- Payoffs
Firms receive \(\Pi_i\) as on previous slide
Workers receive \(\Pi_j = 100 A_j - 40 |C_j - A_j| + \sum_{i=1}^5W_{ij}\) where \[W_{ij} = \begin{cases}100w_{ij} & \text{with probability }80\%\\\bar{w}_j & \text{with probability } 20\%\end{cases}\]
Employers know if \(W_{ij} = 100 w_{ij}\) before setting it!
Mobius and Rosenblat (2006)
Results
Beauty does not affect actual performance, but \(\uparrow\) confidence
Beauty premia, but no taste-based discrimination
B V O VO FTF BEAUTY 0.017 0.131** 0.129** 0.124** 0.167** (0.040) (0.042) (0.034) (0.036) (0.043) SETWAGE -0.010 -0.072 0.098* -0.046 0.033 (0.055) (0.052) (0.046) (0.048) (0.057) SETWAGE x BEAUTY -0.058 -0.099+ 0.005 -0.022 -0.044 (0.057) (0.053) (0.048) (0.050) (0.058) N 163 161 163 162 163 Source: Table 4 (Mobius and Rosenblat 2006)
Beauty premium: 15-20% due to confidence, 40% - stereotype
Rao (2019)
Field and lab experiments eliciting taste-based discrimination
\(\Delta\) policy in India: elite schools offer free places to poor students
Exploit staggered implementation using DiD
- more charitable
- changes fundamental notions of fairness and generosity
- reduce discrimination (teammate choice in race)
- high stakes: only 6% choose slower rich over faster poor student
- low stakes: 33% discriminate against poor students
- past exposure \(\downarrow\) taste discrimination WTP by 12pp
Doleac and Hansen (2020)
Quasi-random policy experiment measuring statistical discrimination
Ban-the-box (BTB) policy
- Banning prior criminal convictions box on job applications
- Hawaii in 1998 \(\longrightarrow\) 34 states + DC in 2015
BTB “does nothing to address the average job readiness of ex-offenders”.
Therefore, statistical discrimination may \(\uparrow\)
Use DiD to measure effect of BTB on employment of minorities
Doleac and Hansen (2020)
| Full sample | BTB-adopting | |
|---|---|---|
| White x BTB | -0.003 | -0.005 |
| (0.006) | (0.008) | |
| Black x BTB | -0.034** | -0.031** |
| (0.015) | (0.014) | |
| Hispanic x BTB | -0.023* | -0.020 |
| (0.013) | (0.015) | |
| Obs. | 503,419 | 231,933 |
| Pre-BTB baseline | ||
| White | 0.8219 | 0.8219 |
| Black | 0.677 | 0.677 |
| Hispanic | 0.7994 | 0.7994 |
Source: Table 4 (Doleac and Hansen 2020)
Glover, Pallais, and Pariente (2017)
Capturing self-fulfilling prophecy of statistical discrimination
Quasi-random assignment of new cashiers to managers in French stores
Do minority cashiers perform worse with biased managers?
Measure manager bias using Implicit Association Test (IAT)
- 66% moderate to severe bias
- 20% slight bias
Outcomes: absences, time worked, scanning speed, time between customers
Glover, Pallais, and Pariente (2017)
| Absences | Overtime (min) | Scan per min | Inter-customer time (sec) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minority x Mngr bias | 0.012*** | -3.237* | -0.249** | 1.360** |
| (0.004) | (1.678) | (0.111) | (0.665) | |
| Obs. | 4,371 | 4,163 | 3,601 | 3,287 |
| Dep var mean | 0.0162 | -0.068 | 18.53 | 28.7 |
Sources: Tables III and IV (Glover, Pallais, and Pariente 2017)
Bohren, Hull, and Imas (2025)
Role of gendered recommendation letters on hiring
- LLM: “female” and “male” recommendation letters
- Fictitious CVs with “male” and “female” names
- Survey 396 hiring managers
| Recommendation gender | ||
| CV name | CV | CV |
| CV | CV |
Bohren, Hull, and Imas (2025)


Summary
Two main frameworks with different implications for labour markets
- Taste-based discrimination
- Statistical discrimination
Systemic discrimination accumulating over time
Simple decomposition to measure unexplained gap
Vast experimental and quasi-experimental literature
Next lecture: Intergenerational mobility on 24 Sep